Email: [email protected]
 2025.11.14
2025.11.14
 Industry News
Industry News
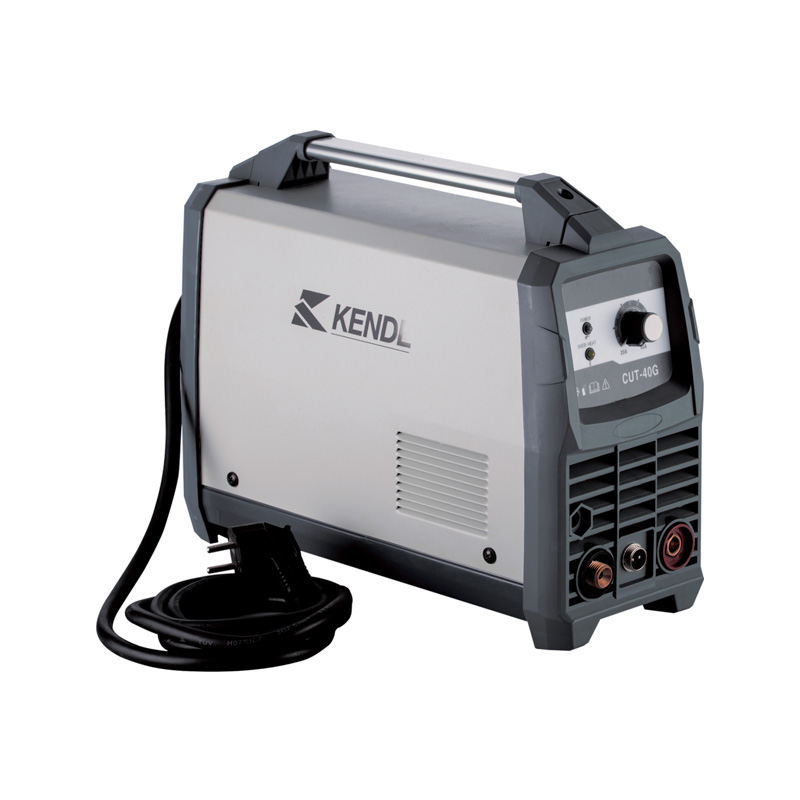

Plasma cutting has become a widely used method for cutting metals in various industries. Inverter Plasma Cutters, in particular, have gained attention for their compact size, energy efficiency, and portability. However, a common question among professionals is whether these devices can handle heavy industrial applications that demand consistent precision and high output.
How Inverter Plasma Cutters Work
Inverter Plasma Cutters differ from traditional plasma cutters in the way they convert power. Using advanced electronics, they transform standard electrical input into a high-frequency output suitable for plasma cutting. This allows the machine to generate a stable and concentrated plasma arc capable of cutting through various metals, including steel, aluminum, and copper. The inverter technology also enables more efficient energy use, reduces heat generation, and allows for more compact machine designs compared to conventional transformer-based cutters.
Cutting Capacity and Thickness
A key factor in industrial applications is the cutting capacity. Inverter Plasma Cutters are available in different power ratings, typically ranging from 40A to over 200A. The cutting thickness depends on both the amperage and the quality of the consumables used. For moderate industrial tasks, such as cutting sheet metal or structural components, these machines can provide precise and clean cuts. For very thick materials, higher-rated models or multiple passes may be necessary to maintain cut quality and speed. Businesses need to match the cutter's specifications with their material requirements to ensure consistent performance.
Precision and Control
Precision is another area where Inverter Plasma Cutters excel. Their electronic controls provide a stable arc, reducing dross formation and minimizing material waste. This is particularly valuable in industrial settings where consistent tolerances are required for assembly or fabrication. The portability of inverter models also allows operators to move the cutter to various work sites or large panels, improving workflow efficiency while maintaining accuracy.
Durability and Industrial Use
Concerns about durability often arise when considering inverter technology for heavy-duty tasks. Modern Inverter Plasma Cutters are designed with robust components and cooling systems to handle continuous operation. Many models include overheat protection, voltage stabilization, and durable housings, which enhance reliability in industrial environments. While they may not always replace large transformer-based machines for extremely high-volume cutting, they are capable of supporting a wide range of heavy-duty industrial applications effectively.
Cost and Efficiency Advantages
In addition to performance, Inverter Plasma Cutters offer cost and efficiency benefits. They consume less power than traditional plasma cutters and typically require less maintenance. The ability to handle both light and moderately heavy industrial tasks with a single machine can reduce the need for multiple cutting tools, lowering overall operational costs. This makes inverter models particularly attractive for workshops and small to medium-sized fabrication operations.
Inverter Plasma Cutters can indeed handle a variety of heavy industrial applications, provided that their specifications match the task at hand. Their stable plasma arc, precise control, and efficient power use make them suitable for cutting metals of moderate thickness while maintaining high quality. While extremely thick or high-volume cutting may require specialized equipment, modern inverter cutters offer a versatile and reliable solution for many industrial scenarios. Businesses that select the appropriate model can benefit from increased efficiency, reduced energy consumption, and improved workflow flexibility.